By 2022, experts predict an increase in the volume of global traffic by almost three times: presumably, the indicators will reach 4.8 zettabytes. As you can imagine, this inevitably leads to an increase in the load on the data centers. This is why there is an increasing need to use a cloud load balancer. This technology is especially actively used in the cloud environment, which, after the start of the pandemic, is developing faster than other industries.
Balancers have been around for quite some time, but as companies tap into private or public clouds, their popularity only grows. At the same time, the technology is undergoing significant changes, which make it possible to increase its efficiency and, at the same time, reduce the cost of its use. Let’s figure out what is the advantage of using balancers and what the modern market can offer.
Why Do You Need a Cloud Load Balancer?
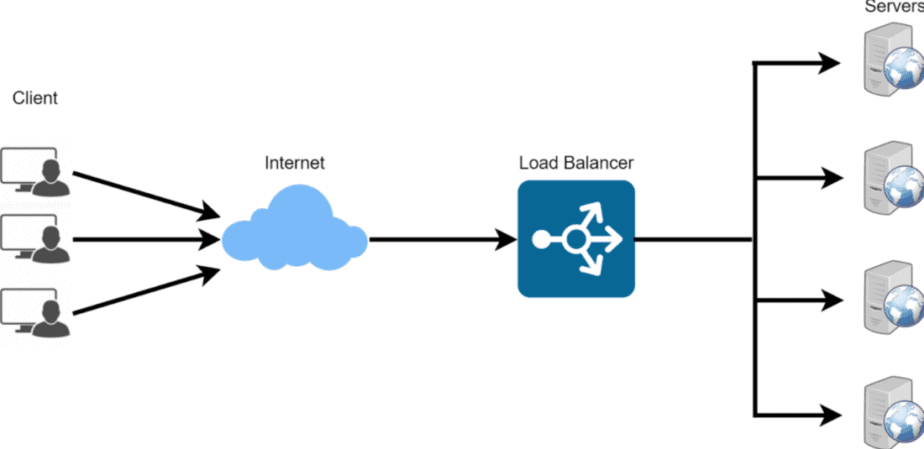
BN (Load Balancer) is a solution to avoid overloading the server. In essence, such a system distributes the incoming traffic among the internal servers used (often referred to as a “farm” or pool).
The operation itself is performed using a physical or virtual device, which selects a suitable server from the pool. This avoids overloading the entire system while simultaneously providing failover between different devices. This allows you to avoid system failures even if one or more servers fail. Workloads are quickly redistributed to redundant devices to help avoid disaster and business disruption.
Load Balancer optimizes resource utilization and delivers quality applications. In addition, the load balancing system manages the incoming flow of information between local/cloud storage and the target PC. In parallel, it allows you to continuously check the operation of servers. If necessary, damaged devices are automatically removed from the pool.
The balancer has various application delivery controllers that ensure the security of the connection. They are used to encrypt and authenticate devices, which allows you to monitor the operation of all services.
The system also includes a number of additional functions:
- Unloading functionality. Allows you to protect the system from DDoS attacks.
- Predictive analytics. Helps to identify and prevent “bottleneck” traffic zones.
- Launching virtual storage. Occurs after exceeding the limits of incoming traffic.
Both hardware and software are used as BN. Hardware devices are physical hardware that runs on top of certain software. As traffic grows, there is the inclusion of additional devices to handle the entire amount of data.
Cloud Load Balancer Benefits
Modern IT systems must meet three basic requirements:
- Flexibility. Many companies are trying to get as much functionality as possible while simultaneously reducing the time it takes to set it up. Therefore, more and more often, public cloud services are used to create infrastructure.
- Efficiency. You will need to complete a large number of tasks with minimal cost. With these goals, the use of infrastructures based on IaaS becomes optimal. This solution allows to take into account the availability and efficiency of operations and also has a positive effect on their cost.
- Multi-cloud procedures. Many organizations choose to store all data in their own data centers. However, you have to solve several tasks using the cloud infrastructure, as this allows for high efficiency. You can’t store confidential information in public cloud services, so the use of private systems is necessary.
Programs and applications have become more sophisticated, customer needs have grown, and traffic has increased markedly. This led to the fact that more and more organizations began to use the cloud infrastructure in their work. Load balancing in such IT systems has become almost mandatory, as it is with its help that it is possible to increase performance and reliability. However, with the speed of the cloud and the ease of scaling, companies can handle peak workloads without significant performance degradation.
Previously used hardware load balancers simply could not cope with the load as the traffic increased. Because of this, providers had to expand the pool of devices and optimize the hardware. Therefore, cloud solutions are replacing traditional load balancers.
Such systems allow you to automatically distribute incoming traffic based on predefined rules. This expands the possibilities of using and maintaining programs, increasing their availability and security.
Advanced Cloud Balancing Benefits
Advanced cloud load balancing has advantages, among which are the following:
Better visibility and data analytics
Thanks to BN, the company better understands the current traffic situation, which solves a number of tasks and facilitates information analytics. It makes it easier to monitor inbound traffic so that you can track the statistics you need.
The company receives detailed reports on server performance and has a better understanding of how the IT infrastructure works. In addition, it is possible to track any malfunctions in the work and determine the cause of their occurrence. This allows the noticing traffic latency issues before users do so.
Providing comprehensive security
The Load Balancer is placed directly in the traffic flow. Thanks to this, you can distinguish between good and bad traffic and automatically detect any attacks and anomalies. This stops malicious traffic and increases the security of the entire infrastructure.
In addition, load balancers have integrated protection, which allows the company to significantly save on additional applications. The configuration of security products is greatly simplified, and it is possible to increase the protection of critical functions.
Automation
More than 70% of companies today use a multi-cloud environment. This is why automation and integration into multiple cloud systems is so important. Load balancing in the cloud involves integration into public and private environments. Most solutions today have APIs for integration.
This enables companies to implement continuous delivery pipelines as well as interoperability with DevOps tools. Moreover, in some cases, it is possible to provide full integration, which you can achieve precisely through the use of the API. DevOps functionality allows you to call API to balance traffic. And BN, in turn, calls an external API to warn a number of events.
Container integration
More and more organizations are adopting containers and container orchestration systems in their IT infrastructure. Many applications are moving to a microservice architecture, moving away from a monolithic environment. This leads to the deployment of systems in virtual machines, which often run in the cloud or multi-cloud environment.
Centralized management
A cloud load balancer provides centralized management of the system, which saves time and avoids configuring individual devices. In the management console, you can see the entire pool of used devices and make general settings. This helps to improve efficiency and achieve ease of operation.
In addition, the BN provides high throughput of the system. This is available through special software running on special processors. The company gains the opportunity to reduce infrastructure costs as cloud balancers typically require fewer resources and are more flexible. The organization does not need to purchase and maintain physical machines, in addition, there is the possibility of scaling the initial volume.
Cloud Load Balancer Operation Scheme
Cloud balancers track the load on the infrastructure using listeners. They use special network protocols to track and validate client requests. Manages to handle many concurrent connections while making all services available at the same time.
During operation, the Load Balancer determines the health of the VM and directs the maximum traffic to them. All non-working instances are instantly removed from the pool, and the load is evenly distributed among the remaining ones.
Planned load balancing is critical to the efficiency of your IT infrastructure. When choosing a balancer, a company should consider the microservices architecture and data center container deployment. Selection criteria should include the ability to integrate with a range of technologies, as well as automatic scaling and support for device visibility.